AJAX 是什么?
5月 2, 2022
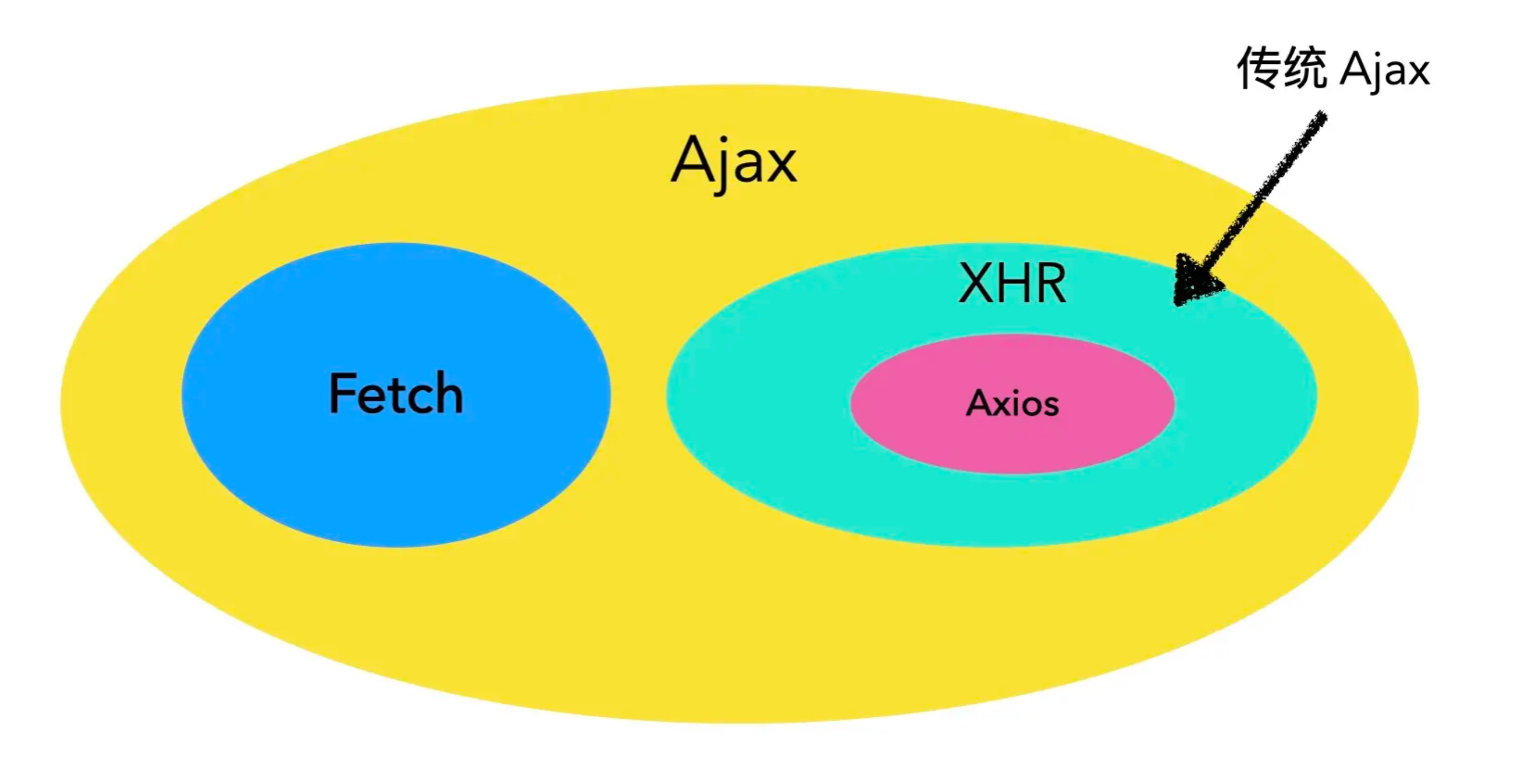
这个问题既熟悉又有点陌生,先看概念。AJAX 是 Asynchronous Javavascript XML 的缩写,即异步 JavaScript 和 XML。使用 AJAX 技术可以在无需重新加载整个网页的情况下,能够更新部分网页,从而给带来更好的用户体验。另外 AJAX 不仅使用 XML,实际上由于 JSON 结构的易读和轻量反而更受欢迎。
AJAX 不是一种单一的技术,而是利用了一系列相关的技术:
- 使用 CSS 和 HTML 来表示信息。
- 使用 DOM 模型来交互和动态显示。
- 使用 XMLHttpRequest 或 Fetch API 来和服务端进行异步通信。
- 使用 JavaScript 来操作 DOM 模型。
你可能发现,上面第 3 条的技术比如 Fetch API 是近几年的技术,而 XMLHttpRequest 才是浏览器传统网络请求技术,故之所以一开始对 AJAX 又陌生,也是因为 AJAX 的概念是在不断更新的,其涵盖的范围在不断扩大。
XMLHttpRequest #
实现传统 AJAX 的核心是 XMLHttpRequest 对象,该对象为客户端提供了在客户端和服务器之间传输数据的功能。
使用方法 #
初始化 #
创建一个 XMLHttpRequest 对象:
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
建立连接 #
使用 open() 方法建立连接:
open(method, url)
open(method, url, async)
open(method, url, async, user)
open(method, url, async, user, password)
method:表示请求使用的方法,比如GET或POST;url:表示请求的服务器地址。async:可选,表示是否异步执行,默认为true;user:可选,password:可选。
发起请求 #
使用 send() 方法向服务器发送数据:
send()
send(body)
如果不传 body 参数,默认就是 null。
响应处理 #
The
readystatechangeevent is fired when thereadyStateattribute of a document has changed.
XHR 提供了 readystatechange 事件用来监听 xhr.readyState 属性发生变化时触发。xhr.readyState 的枚举如下:
| Value | State | Description |
|---|---|---|
0 | UNSENT | Client has been created. open() not called yet. |
1 | OPENED | open() has been called. |
2 | HEADERS_RECEIVED | send() has been called, and headers and status are available. |
3 | LOADING | Downloading; responseText holds partial data. |
4 | DONE | The operation is complete. |
除了 readystatechange 事件,XMLHttpRequest 也支持一系列其他的事件,可自行查阅文档。
xhr.addEventListener("readystatechange", function () {
if (this.readyState === this.DONE) {
console.log(this.responseText);
}
});
//也可以使用事件处理器 onload
xhr.onload = function() {
if (xhr.status != 200) { // 分析响应的 HTTP 状态
alert(`Error ${xhr.status}: ${xhr.statusText}`); // 例如 404: Not Found
} else { // 显示结果
alert(`Done, got ${xhr.response.length} bytes`); // response 是服务器响应
}
};
当 readyState 变为 Done 时,就说明收到了响应,于是进行回调,也是通过此类回调函数的机制实现了异步处理。
嫌麻烦?上 jQuery #
如果上面一系列的步骤你还是嫌麻烦,上古的 jQuery 也提供了 jQuery.ajax() 实现对 XHR 的封装。
$("button").click(function(){
$.ajax({url:"demo_test.txt",success:function(result){
$("#div1").html(result);
}});
});
回调地狱 #
事件回调机制的形式在实际的项目中可能会导致“回调地狱”的情况,处理 error 时需要格外注意。

Fetch #
The global
fetch()method starts the process of fetching a resource from the network, returning a promise which is fulfilled once the response is available.
现在浏览器中的应用更多使用的可能是 Fetch API,它提供了几乎和 XMLHttpRequest 相同的功能,但被设计成更具可拓展性和高效性。
浏览器全局函数 fetch() 用于请求一个网络资源,并通过 promise 异步的形式返回 response 对象,而且可以简化成 async/await 形式,更加符合现代前端技术的设计哲学。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Example</title>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.slim.min.js"
integrity="sha256-u7e5khyithlIdTpu22PHhENmPcRdFiHRjhAuHcs05RI="
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<button type="button" onclick='request();'>请求</button>
<br />
<div id="output"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
async function request(params) {
let response = await fetch("https://httpbin.org/get");
if (response.ok) {
let resp = await response.json();
output(JSON.stringify(resp));
} else {
output("HTTP-Error: " + response.status);
}
}
function output(msg) {
$("#output").append("<p>" + msg + "</p>");
}
</script>
</html>
很多前端项目专门封装的网络层可能会采用以下的形式:
const data = { username: 'example' };
fetch('https://example.com/profile', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify(data),
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log('Success:', data);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('Error:', error);
});
跨域问题 #
默认情况下,Ajax 要满足浏览器的同源策略要求,即不能跨域访问,除非客户端使用 CORS 标准进行请求,我前面已经在 跨域相关问题 里介绍了其使用方法,只有符合了请求相关规范,并在服务器同意的情况下才能发起跨域访问。