介绍 #
堆(heap)分为最大堆(大根堆/大顶堆)和最小堆(小根堆/小顶堆),通常用完全二叉树实现,完全二叉树又可以用数组实现,故堆通常以数组形式进行存储,而非二叉树的链式存储。常见的堆有二叉堆、裴波那契堆等,通常也用堆来实现优先队列(Priority Queue)。
堆的特点 #
堆属性非常有用,因为堆常常被当做优先队列使用,因为可以快速地访问到“最重要”的元素。
- 在最大堆中,父节点的值比每一个子节点的值都要大。
- 在最小堆中,父节点的值比每一个子节点的值都要小。
- 满足完全二叉树的特性:在当前层级所有的节点都已经填满之前不允许开始下一层的填充。
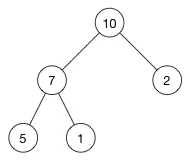
如图,这是一个最大堆,转化为数组之后:[ 10, 7, 2, 5, 1 ],故堆的查找的时间复杂度为 O(1)。
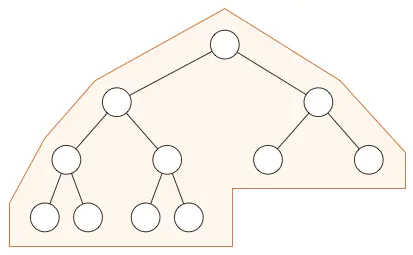
在堆中,在当前层级所有的节点都已经填满之前不允许开始下一层的填充,所以堆总是有这样的形状:
基于二叉堆的性质,当数组的第一个空着,arr[1] 为根节点时,每个节点的父节点和左右孩子的索引都可以通过简单的运算得到:
// 父节点的索引
int parent(int root) {
return root / 2;
}
// 左孩子的索引
int left(int root) {
return root * 2;
}
// 右孩子的索引
int right(int root) {
return root * 2 + 1;
}
以 arr[0] 为根节点时:
parent(i) = floor((i - 1)/2)
left(i) = 2i + 1
right(i) = 2i + 2
堆和树的区别 #
节点的顺序在二叉搜索树中,左子节点必须比父节点小,右子节点必须必比父节点大。但是在堆中并非如此。在最大堆中两个子节点都必须比父节点小,而在最小堆中,它们都必须比父节点大。
内存占用普通树占用的内存空间比它们存储的数据要多。你必须为节点对象以及左/右子节点指针分配内存。堆仅仅使用一个数组来存储数据,且不使用指针。
平衡二叉搜索树必须是“平衡”的情况下,其大部分操作的复杂度才能达到 O(log n) 。你可以按任意顺序位置插入/删除数据,或者使用 AVL 树或者红黑树,但是在堆中实际上不需要整棵树都是有序的。我们只需要满足堆属性即可,所以在堆中平衡不是问题。因为堆中数据的组织方式可以保证 O(log n) 的性能。
搜索在二叉树中搜索会很快,但是在堆中搜索会很慢。在堆中搜索不是第一优先级,因为使用堆的目的是将最大(或者最小)的节点放在最前面,从而快速的进行相关插入、删除操作。
常用操作 #
以最大堆为例。
堆的插入、删除操作都可能需要交换节点,以便把节点放到合适的位置,交换的次数最多为二叉树的深度,因此如果堆中有n个节点那么它的插入和删除操作的时间复杂度都是 O(logn) 。
插入结点 #
步骤如下:
- 在最大堆中添加新的节点,应该先从上到下、从左到右找出第 1 个空缺的位置,并将新节点添加到该空缺位置。
- 如果新节点的值比它的父节点的值大,那么交换它和它的父节点。
- 重复这个过程,直到新节点的值小于或等于它的父节点,或者它已经到达堆的顶部位置。
新结点上浮的过程叫 swim 上浮。
删除结点 #
通常只删除对顶部的元素,步骤如下:
- 将堆最底层最右边的结点移到堆的顶部。
- 如果此时它的左子节点或右子节点的值大于它,那么它和左右子节点中值较大的节点交换。
- 如果交换之后节点的值仍然小于它的子节点的值,则再次交换,直到该节点的值大于或等于它的左右子节点的值,或者到达最低层为止。
这里结点下沉的过程叫 sink 下沉 。
各语言实现 #
除了 Java / Golang,一般都需要自己实现一个堆类用来初始化实例,尤其是所用语言的标准库没有帮你实现的情况下。
golang #
go 内置了 container/heap 实现堆,实现这个 interface 的实例就可看做是一个堆。
type Interface interface {
sort.Interface
Push(x any) // add x as element Len()
Pop() any // remove and return element Len() - 1.
}
初始化一个堆:
package main
import (
"container/heap"
"fmt"
)
// An IntHeap is a min-heap of ints.
type IntHeap []int
func (h IntHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h IntHeap) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i] < h[j] }
func (h IntHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *IntHeap) Push(x any) {
// Push and Pop use pointer receivers because they modify the slice's length,
// not just its contents.
*h = append(*h, x.(int))
}
func (h *IntHeap) Pop() any {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}
// This example inserts several ints into an IntHeap, checks the minimum,
// and removes them in order of priority.
func main() {
h := &IntHeap{2, 1, 5}
heap.Init(h)
heap.Push(h, 3)
fmt.Printf("minimum: %d\n", (*h)[0])
for h.Len() > 0 {
fmt.Printf("%d ", heap.Pop(h))
}
}
// minimum: 1
// 1 2 3 5
常见题型 #
TopK 问题 #
TopK 问题可总结有三种解法:
- 排序,比如快速排序。
- 局部排序,比如冒泡排序,但是只冒 K 个泡。
- 堆,只找到 TopK,但并不排序。
用堆实现时,先用前 k 个元素生成一个最小堆,接着从数组第 k+1 个元素开始,和堆顶的元素做比较并判断是否要换掉堆顶,数组遍历完成后堆中的元素就是最大的 K 个元素。
相关问题 #
斐波那契堆 #
堆排序 #
参考本站另一篇 排序算法
优先队列 #
普通队列遵循先进先出,优先队列的出队顺序取决于“优先级”(一般是按大小排序),和入队顺序无关,通常用二叉堆实现优先队列(Priority Queue),也有二项堆、平衡树、线段树等其他方式实现。
优先队列的使用场景还挺多:
- 数据压缩:赫夫曼编码算法;
- 最短路径算法:Dijkstra算法;
- 最小生成树算法:Prim算法;
- 事件驱动仿真:顾客排队算法;
- 选择问题:查找第k个最小元素;
优先队列的性质是,队列是排好序的。插入或删除元素的时候,元素会自动排序。
func (pq *PriorityQueue) Push(x any) {
n := len(*pq)
item := x.(*Item)
item.index = n
*pq = append(*pq, item)
}
func (pq *PriorityQueue) Pop() any {
old := *pq
n := len(old)
item := old[n-1]
old[n-1] = nil // avoid memory leak
item.index = -1 // for safety
*pq = old[0 : n-1]
return item
}
// update modifies the priority and value of an Item in the queue.
func (pq *PriorityQueue) update(item *Item, value string, priority int) {
item.value = value
item.priority = priority
heap.Fix(pq, item.index)
}
// This example creates a PriorityQueue with some items, adds and manipulates an item,
// and then removes the items in priority order.
func main() {
// Some items and their priorities.
items := map[string]int{
"banana": 3, "apple": 2, "pear": 4,
}
// Create a priority queue, put the items in it, and
// establish the priority queue (heap) invariants.
pq := make(PriorityQueue, len(items))
i := 0
for value, priority := range items {
pq[i] = &Item{
value: value,
priority: priority,
index: i,
}
i++
}
heap.Init(&pq)
// Insert a new item and then modify its priority.
item := &Item{
value: "orange",
priority: 1,
}
heap.Push(&pq, item)
pq.update(item, item.value, 5)
// Take the items out; they arrive in decreasing priority order.
for pq.Len() > 0 {
item := heap.Pop(&pq).(*Item)
fmt.Printf("%.2d:%s ", item.priority, item.value)
}
}
// 05:orange 04:pear 03:banana 02:apple
参考 #
https://www.jianshu.com/p/6b526aa481b1